8 Ways To Heal a Dysregulated Nervous System To Get Out Of Survival Mode
A dysregulated nervous system is a state in which the body struggles to shift between activation (fight-or-flight) and restoration (rest-and-digest), leading to chronic anxiety, emotional reactivity, shutdown, or exhaustion.
You wake up tired even after sleeping; little compliments seem touchy; loud noises make your chest shrink. Calm down, you tell yourself, but your body doesn’t listen. “What’s wrong with me?” you ask.
The problem with healing a dysregulated nervous system is not weakness. It’s a state of confusion. In addition to being tired, you feel tense. Despite your desire for peace, your body remains on high alert, as though something is going to happen.
This misconception is that people think stress is the issue. However, the truth is that your nervous system no longer feels secure. Your nervous system also reacts before you realise it when it senses danger.
What is the Dysregulated Nervous System?
When your nervous system is dysregulated, your body’s stress response either remains active for an extended period or shuts down too quickly. After pressure, it has trouble regaining equilibrium. You need a balanced neurological system to recognise and control your emotions without letting them rule you. Regulating emotions is more difficult when the body is unstable.
According to research based on Dr. Stephen Porges’ Polyvagal Theory, your neural system continuously looks for danger or safety, without your conscious knowledge1. According to Porges (2011), it automatically switches into fight, flight, or freeze when it perceives danger. Chronic stress also alters brain circuits involved in fear and emotional regulation, according to studies by Harvard Medical School (McEwen, 2017)2.
Additionally, research in Frontiers in Psychology confirms that emotional regulation skills strongly predict nervous system resilience3.
So the real question becomes: how do you heal a dysregulated nervous system when the body itself feels like the problem?
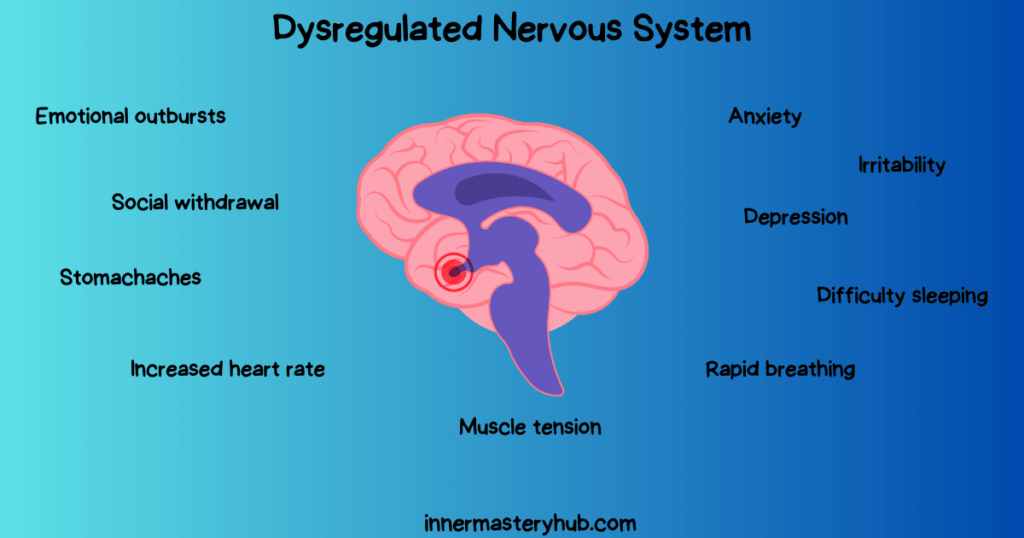
Signs of Dysregulated Nervous System
A healthy autonomic nervous system maintains homeostasis. Dysregulated nerve systems can cause many physical and emotional disorders.
Physical symptoms
- Increased heart rate
- Rapid breathing
- Muscle tension
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Headaches
- Stomachaches
- Pain
Emotional symptoms
- Anxiety
- Irritability
- Depression
- Difficulty concentrating
- Difficulty sleeping
- Emotional outbursts
- Social withdrawal
Causes of a dysregulated nervous system
A dysregulated nervous system can be caused by several factors, including:
Chronic Stress
Your Cortisol levels remain high due to ongoing stress from caregiving, relationships, employment, and money. This ongoing stimulation gradually weakens the body’s capacity to return to baseline calm. Prolonged stress has been shown to alter brain regions involved in danger sensing and emotional regulation (McEwen, 2017).
Any trauma
Trauma is not just significant occurrences. Unpredictable caring, bullying, emotional neglect, and repeated criticism can teach the nervous system to look for threats. The Polyvagal Theory of Dr. Stephen Porges states that the body naturally adjusts to perceived threats, generally without conscious knowledge.
Childhood Attachment Insecurity
Your nervous system learns whether the environment is secure from early relationships. Later in life, hypervigilance or shutdown habits can result from carers who are inconsistent or emotionally unavailable.
Suppression of Emotions
Healthy stress release is prevented when emotions are consistently ignored. The body retains the activation when emotions are not handled, leading to dysregulation.
Lack of Rest and Recovery
Poor sleep, overwork, and constant digital stimulation prevent the parasympathetic nervous system (the calming branch) from restoring balance.
Medical Conditions and Hormonal Imbalances
Thyroid disorders, chronic inflammation, autoimmune conditions, and hormonal shifts (such as postpartum or menopause) can disrupt nervous system regulation.
What Does It Mean to Heal a Dysregulated Nervous System?
Helping your body regain its flexibility so it can react to stress and then safely rest again is the goal of healing a dysregulated nervous system. Never experiencing stress is not the goal of regulation. The goal is to manage it without being stuck.
A dysregulated system either remains in Survival Mode or collapses into a shutdown state, whereas a regulated system seamlessly transitions between activation and rest. This natural rhythm is restored through healing.
Why Does the Nervous System Become Dysregulated?
Recurrent stress, trauma, emotional neglect, or prolonged pressure without healing can all lead to a dysregulated neural system. The body can learn to remain vigilant even in the face of modest events, such as growing up without emotional protection.
This is often how it works: a trigger happens, your brain perceives it as a threat, your body generates stress hormones, and eventually, even in the case of a minor threat, the reaction becomes routine.

How Does Emotional Regulation Connect to Nervous System Healing?
The ability to recognise and understand emotions, and to behave sensibly rather than impulsively, is known as emotional control. But if your body feels insecure, you can’t control your emotions adequately.
The prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for reasoning, remains active when the nervous system is at ease. The amygdala, which senses danger, takes over when it is dysregulated. Therefore, emotional regulation is immediately improved by nerve system restoration.
How to Heal The Dysregulated Nervous System?
It is not necessary to “calm down” in order to heal a dysregulated neurological system. It involves telling your body that it is safe once more. Emotional regulation naturally increases when your nervous system learns safety via repeated experiences.
Here is a straightforward strategy supported by research.
1. Recognise the changes taking place in your body
Your stress response, fight, flight, or freeze, activates too quickly and continues for too long if your neurological system is dysregulated. Your nervous system continuously looks for danger or safety without your conscious knowledge, according to Dr. Stephen Porges’ Polyvagal Theory.
When you stop criticising your reactions and begin to see them as defensive responses, healing can begin. From “What’s wrong with me?” to “What is my body protecting me from?”
2. Regulate Through the Body First
When you are dysregulated, logic alone cannot calm you because stress hormones override reasoning. Research shows slow breathing activates the vagus nerve, which supports the parasympathetic (calming) system.
- Slow, extended exhale breathing (inhale 4, exhale 6)
- Gentle stretching or yoga
- Cold water on the face
- Slow walking in nature
These signals tell the body that danger has passed.
3. Improve Emotional Regulation Skills
Emotional regulation means noticing feelings without being controlled by them. Studies published in Frontiers in Psychology show that people with stronger emotional regulation skills experience lower stress reactivity.
Try:
- Naming emotions (“I feel anxious” instead of “I am anxious”)
- Journaling triggers and patterns
- Practicing self-compassion during activation
Naming feelings reduces amygdala activation in the brain.
4. Create Predictable Safety in Daily Life
Your nervous system heals through consistency. Unpredictability increases threat perception.
Focus on:
- Regular sleep schedule
- Balanced meals
- Reducing caffeine
- Structured daily routines
Small stability signals accumulate over time.
5. Heal Through Safe Relationships (Co-Regulation)
Humans regulate each other. Warm eye contact, calm voices, and empathetic presence activate calming neural pathways.
If possible:
- Spend time with emotionally safe people
- Consider trauma-informed therapy
- Join support groups
Connection is not optional for healing; it is biological medicine.
6. Reduce Chronic Stress Load
Chronic stress reshapes brain circuits linked to fear and emotional control (McEwen, 2017, NIH)4. You cannot heal if activation never pauses.
Reduce unnecessary stressors where possible:
- Set boundaries
- Limit overstimulation (news, social media)
- Schedule recovery time
Healing requires recovery cycles.
7. Address Trauma Gently
If trauma is present, healing may require professional support. Somatic therapies, EMDR, or trauma-informed counseling can help the body process stored survival responses safely.
The goal is not to relieve pain but to complete unfinished stress responses.
8. Strengthen the Window of Tolerance
The “window of tolerance” is the range where you feel calm and functional. Healing expands this window.
Signs it is growing:
- Faster recovery after stress
- Less emotional overwhelm
- More choice in responses
This growth happens gradually, not overnight.
Advice like “just think positive” fails because dysregulation is physiological. When cortisol and adrenaline are high, reasoning shuts down. You must calm the body before reshaping thoughts.
Can a Nervous System Dysregulation Be Healed Without Trauma?
Indeed. Not all trauma is dramatic. The system becomes dysregulated due to ongoing stress, exhaustion, or emotional invalidation. Research indicates that the sympathetic nervous system is more activated when people experience chronic job stress, keeping the body in a fight-or-flight state (American Psychological Association, 2022)5.
Restoring safety signals is part of healing, not merely getting rid of severe trauma.
How Long Does It Take to Heal a Dysregulated Nervous System?
Healing is not linear. Because the nervous system learns through repetition, change requires consistent safety experiences. Some people notice improvement in weeks, while deeper patterns can take months or longer.
The shift in perception of when your body begins to experience calm without immediately scanning for danger is a strong sign that your nervous system is healing.
What Are Signs Your Nervous System Is Healing?
You react less intensely to small stressors. You recover faster after a conflict. Your sleep improves. You feel more present. Healing is steady. It feels like the space between trigger and response. It feels like a choice returning.
How Do Famous Thinkers Explain Nervous System Struggles?
Carl Jung said that we are controlled from within by the things we do not consciously confront. “Your life will be guided by the unconscious, which you will label as fate, until you bring it into consciousness,” he wrote. Dysregulation shapes reactions before awareness is even present.
Viktor Frankl highlighted the significance of suffering. Finding meaning helps settle internal turbulence by reframing interpretation, whereas pain triggers Survival responses.
Despite his reputation for habits, James Clear emphasises changes in identity. Your healing story shifts when you stop viewing yourself as “broken” and start viewing yourself as adaptive.
Heal a Dysregulated Nervous System by Changing the Story of Safety
You must realise that your body is not broken to heal a dysregulated nervous system. It changed to stay alive. Survival, however, kept you rigid even as it kept you operating.
The change starts when you listen to what your reactions are protecting and stop fighting them. Since healing is about establishing safety so that peace arises organically, it is not about imposing calmness.
If this strikes a chord with you, start observing when your body stiffens and ask yourself softly, “What is my system protecting me from right now?” The first indication of safety is awareness.
Apply this realisation to your day and look for patterns in your behaviour without passing judgement.
FAQS
Effects of a dysregulated nervous system on physical health
A dysregulated nervous system can negatively impact physical health. Chronic stress, a typical result, may contribute to cardiovascular issues, weakened immune function, digestive problems, and musculoskeletal issues. Sleep disturbances and hormonal imbalances may also arise. Addressing nervous system regulation is crucial for maintaining overall physical well-being.
Can Social Connection Heal a Dysregulated Nervous System?
Yes. According to Polyvagal Theory, safe connection signals the nervous system to relax. Eye contact, warm tone, and empathy activate the ventral vagal pathway linked to calm states.
Humans regulate each other. Isolation worsens dysregulation because the nervous system interprets loneliness as a threat.
Why Does Shame Keep the Nervous System Stuck?
Shame tells you something is wrong with you. That belief becomes another trigger.
When you feel ashamed of anxiety or emotional reactions, the nervous system detects danger again, restarting the stress cycle. Self-compassion interrupts this loop by sending internal safety cues.
Does childhood affect nervous system regulation?
Yes, early attachment experiences strongly shape how safe or threatened your system feels in adulthood.
Is dysregulation permanent?
No, the nervous system is plastic and can change through repeated safety experiences.
Can exercise regulate the nervous system?
Moderate, consistent movement helps discharge stress hormones and improves flexibility in stress response systems.
Why do I feel tired and wired at the same time?
This happens when your system swings between fight-or-flight and partial shutdown, creating exhaustion mixed with tension.
Can anxiety mean my nervous system is dysregulated?
Yes, chronic anxiety signals prolonged sympathetic activation, meaning your body remains in fight-or-flight mode even without immediate danger.
How does trauma affect nervous system regulation?
Trauma trains the brain to detect danger faster and more intensely, strengthening survival pathways and weakening calming circuits.
Is nervous system healing the same as therapy?
Not exactly. Therapy can support healing, but regulation also involves body-based awareness, safe relationships, and stress recovery patterns.
- The Autonomic Nervous System’s Secret Language ↩︎
- Neurobiological and Systemic Effects of Chronic Stress ↩︎
- Unraveling the roles of emotion regulation and resilience ↩︎
- Chronic Stress Weakens Connectivity in the Prefrontal Cortex ↩︎
- Stress effects on the body ↩︎






