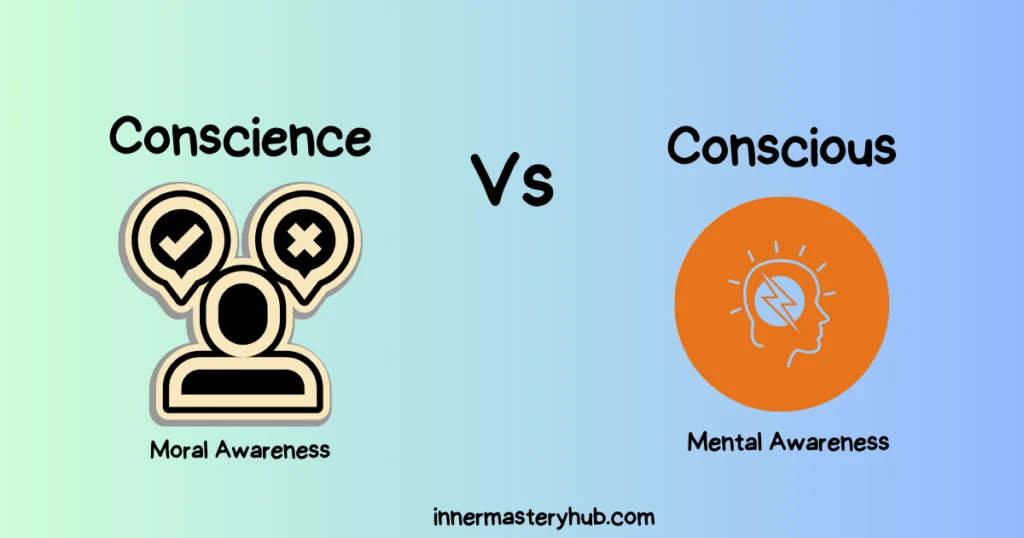
In light of their similar sounds, “Conscience vs. Conscious” is commonly used interchangeably. They signify somewhat different things, though. A person’s internal feeling of good and wrong is called their conscience. The voice in your head is the one that informs you if what you are doing is right or wrong. The term conscious implies “aware” or “alert.” It describes the condition of being mindful of your surroundings and awake.
Let’s have a deeper look into the psychology of Conscience vs. Consciousness
RELATED: Understanding the Vicious Cycle of Shame
Table of Contents
What Does Conscience Mean? Difference between Conscience vs. Conscious
Conscience is an inherent moral compass[1] that guides behavior and helps people choose right from wrong. It’s vital for moral development and decision-making, affecting an individual’s actions and morality. Various factors influence consumer behavior, including parents[2], caregivers, peers, and teachers in early childhood.
Psychologists have proposed many theories about conscience’s origins and function. Freud’s view says that conscience is part of the superego, a moralistic portion of the personality that develops throughout childhood. Freud believed the superego internalizes social norms and expectations and judges an individual’s conduct.
Others emphasize how conscience is influenced by cognitive development[3]. They contend that humans develop their ability to think abstractly and consider consequences as they age. They have a higher mental capacity, which allows them to make moral and ethical decisions.
However, conscience is not always infallible. It can be influenced by biases, emotions, and environmental pressures, leading to actions that may contradict one’s moral compass. Additionally, individuals may repress or dismiss their conscience to achieve personal benefit or avoid unpleasant consequences.
Here are some examples of how conscience can manifest itself in our lives:
- Feeling guilty after cheating on a test.
- Feeling proud after donating to charity.
- Struggling with whether or not to lie to a friend.
- Feeling compelled to speak out against injustice.
RELATED: Cognitive Dissonance: Theory, Examples & How to Reduce It
What Does Conscious Mean?
What it means to be conscious is to be completely aware of your environment, thoughts, and emotions. It’s similar to being aware and awake in the present, comprehending and feeling what’s happening within and outside you.
According to some experts, the ability to express your thoughts about something defines you as conscious of it. Consciousness is an ever-changing entity. Depending on our mental state, physical surroundings, and social contacts, it may alter over time.
Sigmund Freud, the creator of psychoanalysis, believed that consciousness was the highest and most aware level of the mind. It includes all we are conscious of at any given time, including our ideas, feelings, perceptions, and experiences.
According to Freud, conscious awareness only makes up a small portion of the mind, and most mental processes occur subconsciously.
Freud created a mental structural model he dubbed the topographic model. This model divides the mind into three layers: conscious, preconscious, and unconscious.
Freud held that, despite our unconscious awareness, the unconscious mind significantly impacts our conduct.
RELATED: Behavior Chain Analysis
Conscience vs. Conscious
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between consciousness vs. conscience:
| Feature | Conscious | Conscience |
|---|---|---|
| Part of speech | Adjective | Noun |
| Definition | Aware or alert, Mental Awareness | A person’s inner sense of what is right and wrong, Moral Awareness |
| Example | “She was unconscious after the accident.” | “I had a guilty conscience after I cheated on the test.” |
To help you remember the difference between Conscience vs. Consciousness, think of the following:
- Consciousness has to do with being aware of your surroundings.
- Conscience has to do with your moral compass.
What is the connection between Conscience vs. Consciousness?
Consciousness and conscience are two essential components of human morality. Consciousness allows us to perceive the world around us and to understand the consequences of our actions, while conscience guides us toward the right choice. Without consciousness vs. conscience, we could not live ethical lives.
How to Find Your Sense of Self in an Unconscious World
Finding your identity in a society where people are constantly busy can be difficult. First, focus on the values and passions that make you feel a certain way.
Consider your experiences and the lessons they have taught you. Take advantage of your alone time to connect with your inner thoughts. Asking difficult questions and recognizing your strengths and places for improvement will help you become more self-aware.
Be in the company of encouraging people and relationships that reflect who you are. Rediscovering your sense of self in an unconscious world requires a combination of self-reflection, conscious decision-making, and a dedication to remaining faithful to your path.
RELATED: Unmasking Fake Femininity
The dark side of not having a conscience
The moral compass is shadowed or confused when there is no conscience. Without it, people can walk down a dark path without empathy or ethical boundaries. This gap might result in destructive behavior that lacks regret or responsibility. The wrong side of not having a conscience affects people individually and in society when there is a moral void.
RELATED: Unmasking Fake Femininity
Some tips to Develop a Stronger Conscience
Developing a stronger conscience is about becoming more aware of your values and acting in ways that align with those values. Here are a few tips to help you develop a stronger conscience:
- Make time for self-reflection. Spend time each day reflecting on your thoughts, feelings, and actions. Ask yourself questions like: Was I honest today? Did I treat others with respect? What could I have done differently?
- Identify your values. What is important to you in life? What principles do you want to live by? Once you know your values, you can start to make decisions that align with them.
- Accept responsibility for your actions. Nobody is perfect, and everyone makes mistakes. But when you make a mistake, take responsibility for it and try to learn from it.
- Do the right thing, even when it’s complicated. Standing up for what you believe in can be difficult, but it’s essential to do the right thing, even when it’s unpopular.
SOURCES:
- Cote, S. M. Sex Differences in Types of Aggressive Behaviors: Do Women Have a Higher Level of Conscience Than Men? In: W. Koops, D. Brugman, T. J. Ferguson, A. F. Sanders. The Development and Structure of Conscience. New York: Psychology Press; 2010: pp. 287–309.
- Kochanska G, Aksan N. Children’s conscience and self-regulation. J Pers. 2006;74(6):1587-1617. doi:10.1111/j.1467-6494.2006.00421.x
- The role of consciousness in cognitive control and decision-making