What Is Resilience?
The capacity to rebound from trying circumstances or setbacks is Resilience. It is the ability to adjust to and manage stress, adversity, trauma, or tragedy while maintaining good mental health. Being resilient is keeping a positive outlook and attitude, staying adaptable and flexible, and carrying on despite difficulties.
Instead of being a natural quality, Building resilience involves coping skills that can be honed over time with practice, encouragement, a learning attitude, and deliberate effort. Individuals who have to build Resilience feel better capable of handling challenging situations, have greater self-confidence and self-esteem, and lead more satisfying lives. In this article, I will discuss some fantastic factors of “The Power Of Building Resilience.”
Table of Contents
Building Resiliency
Building Resilience entails learning techniques and strategies that permit people to handle stress and adversity and constructively face challenges and obstacles. Here are some methods for increasing Resilience:
Develop a happy outlook by emphasizing optimistic and grateful thoughts and beliefs whenever hard times hit you. Building resilience can aid in changing your viewpoint and fostering a spirit of resiliency and hope. Homo sapience has been born with the most diverse tendencies to cope with every circumstance. You must have felt that way when going through difficult times. Haven’t you?
The challenges in our lives have been set to transform us into resilient versions of ourselves. You would agree, for I have observed much about this human trait throughout my life.
Create a support network by surrounding yourself with kind and understanding individuals, such as friends, extended family, or a therapist. Having a support system can provide one with a sense of community support.
RELATED: Emotional Resilience: 11 Strategies To Build it
Self-care is the act of looking after oneself. Self-care can be practiced by anyone who is kind and compassionate toward others. If you care for yourself in the true sense, then avoiding people’s suffering is impossible. To care for yourself, find things that make you feel calm, centered, and balanced. Exercise, meditation, and enjoyable hobbies can all fall under this category. And remember to serve those who need you if you genuinely care for yourself.
We young adults do; children are not born with Developed problem-solving abilities but can learn to recognize and approach problems proactively. You may feel more assured in managing challenging circumstances due to learning through these situations.
Challenging circumstances always assist you in building resilience and require you to be flexible and adaptable; be ready to modify and adjust to new possibilities by not avoiding face change, transforming you into a more resilient being.
Life will be full of inevitable challenges and difficulties. It is difficult for someone to handle their crisis, sometimes which may include illness, the death of a friend or relationship, abusive behavior, bullying, unemployment, job, or financial instability. There has also been a recurring reality about tragic life events reported daily in the media.
Resilience theories describe how people suffer through difficulties rather than how they respond or adapt to situations such as change, loss, or risk. Resilience theories are often used to study various research fields, such as psychology, human development, and change management.
Benefits and Resources for Building Resilience
Better mental health
Developing Resilience can make it easier for people to deal with stress, anxiety, and despair. It also assists people in keeping a happy mindset and enhancing general well-being.
Productivity gains:
Resilient People can better deal with difficulties and failures, which can enhance productivity and help them succeed in their personal and professional lives.
More effective communication, stronger relationships, feelings, and a connection with others are all benefits of building resilience in people.
Improved problem-solving skills and abilities:
Resilient people can better recognize and address difficulties, develop original solutions, and learn from their experiences.
A greater sense of Resilience involves awareness of self-efficacy and confidence in one’s capacity to overcome obstacles and achieve goals that can be attained through developing resilience.
Inspirational Examples of Building Resilience
Despite their immense challenges, many incredible people have remained determined. Instead, they fought despite the grim situation, which became a solid psychological strength to overcome rejection and become a successful business owner and manager.
After a friend told Campbell that Vogue’s doors were closed for black ladies to be featured, Campbell said he’d open them up. She sent out an ominous statement that no other person could be allowed to reject and hurt her. Instead, she decided by the admission that she’s a beautiful, exciting woman who deserves a place on the cover.
The Top Factors Involve in Building Resilience
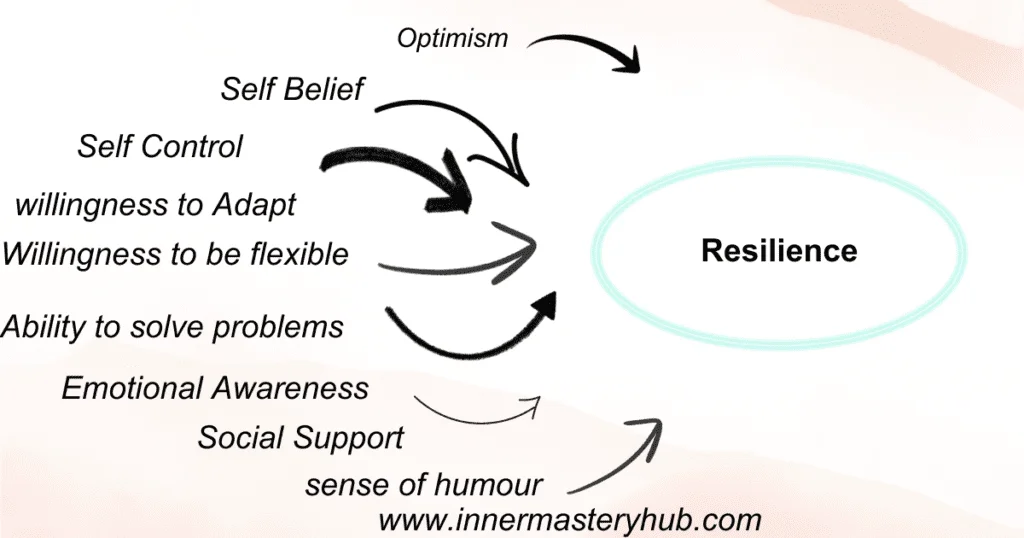
Building Resilience is essential for overcoming obstacles in life and moving forward. The following are some of the main elements that can promote and develop Resilience:
Social support: Surviving difficult times and giving a connection and belonging is possible when you have a strong network of family members, friends, and other helpful people.
Positive self-talk: How you speak to yourself can significantly influence your capacity to handle stress, criticism, and adversity. Talk to yourself kindly and concentrate on your accomplishments and talents.
Flexibility is a critical and crucial component of Resilience because it allows people to adjust and revise their plans when things don’t go according to plan. Open to new concepts and willing to explore various strategies.
Self-care: Taking good care of your body, mind, and emotions is essential for building Resilience. Obtaining enough rest, maintaining a nutritious diet, and participating in enjoyable and relaxing activities.
Problem-solving abilities
An essential component of Resilience is recognizing and addressing issues. Develop your problem-solving skills, and ask for help and direction when necessary.
Optimism: Optimism can help you get through challenging situations and see opportunities for development, success, and progress. Be grateful and keep your attention on the positive aspects of your life.
Inspirational Examples of Incredible Resilience
Nick Vujicic: Nick is an Australian motivational speaker born without arms or legs due to the unusual condition of tetra-amelia syndrome. Nick has traveled the world to spread his message of optimism and endurance despite encountering many obstacles, and his upbeat outlook and tenacity have motivated millions of others.
Nelson Mandela: Nelson Mandela was a revolutionary against apartheid in South Africa who served 27 years in prison. After spending so much time behind bars, Mandela was the first black president of South Africa. During his office, he sought to abolish the apartheid system and advance peace and healing.
Bethany Hamilton is a professional surfer from Hawaii who, at the age of 13, was attacked by a shark and lost her left arm. Despite this setback, Bethany continued surfing and eventually rose to the sport’s top, inspiring young people worldwide with her tenacity and drive.
Stephen Hawking: At age 21, theoretical physicist Stephen Hawking of the United Kingdom received an ALS diagnosis. Hawking maintained his revolutionary cosmology and quantum gravity work despite using a wheelchair and losing his speaking ability. He rose to become one of the most well-known scientists of his era.
Types of Resilience: Psychological, Emotional, Physical, and Community
People and groups can create a variety of forms of Resilience. These consist of the following:
Psychologically resilient is the capacity to handle stress and hardship, such as traumatic experiences or significant life upheavals. Robust, psychologically resilient individuals can maintain a positive mindset and adjust to novel circumstances.
It’s the capacity to control and regulate one’s emotions, particularly under pressure or when facing a challenging situation. Emotional solid regulation and resiliency enable individuals to overcome losses and maintain their dynamic equilibrium.
Physical Resilience: The ability of the body to tolerate and bounce from physical stressors like disease, injury, or other physical problems is referred to as physical resilience. Strong physical resiliency is accompanied by healthy behaviors and practices that promote physical well-being.
Community resilience is the capacity of a community to band together and help one another in the face of stress or adversity. Enormously resilient communities have developed networks and support systems that can assist people and families in coping with and adjusting to disruptive situations.
What Is Psychological Resilience?
Psychological research demonstrates that the resources and skills associated with more positive adaptation (i.e., greater Resilience) can be cultivated and practiced.
According to APA, American Psychological Association
Behavioral flexibility manages hardship, pain, trauma, judgments, criticism, and depression and adjusts to daily hindrances. It’s a crucial quality that enables people to handle pressure and challenging circumstances without losing their mental equilibrium.
Psychological resilience has several facets and includes various attributes, including self-esteem, optimism, problem-solving abilities, emotional control, security, and social support. These elements build strength and defend against the negative impacts of stress and adversity.
High psychological Resilience makes young people better capable of overcoming setbacks, recovering from trauma, and thriving under adverse conditions. They believe they can overcome challenges because they have an optimistic view of life, a purpose, and these qualities. Additionally, they frequently use constructive coping skills and mechanisms like getting social support, working out, or practicing mindfulness.
On the other hand, individuals with low psychological resilience could find it difficult to handle stress and adversity. They might suffer from adverse effects like anxiety, sadness, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). They could feel overtaken by difficulties, have self-doubt, and isolate themselves from others.
What Is Emotional Resilience?
Emotional resilience is the capacity to adjust to and deal with stress, hardship, and other more complex emotions or life circumstances. It involves recovering from setbacks, retaining equilibrium, and even facing pressures or challenging emotions or behaviors.
The emotional resilience of a person can be determined by several factors such as age, identity, or the type of circumstances he or she has gone through in his or her challenging life experiences. For example, people with solid emotional resilience can deal with difficult situations with a positive perspective and go through such times by laughing and confidently.
While less Emotionally Resilient cannot deal with tough times more efficiently, they may fear to proceed, want to be extra cautious, or even try to hide under their shell. Being emotionally resilient entails handling difficulties with resourcefulness, inner strength, and flexibility rather than being resistant to stress or avoiding challenging situations.
Emotionally resilient people can even dare to help others by practicing empathy or compassion. Heart refers to understanding others’ feelings, and compassion means doing something to alleviate their suffering. By using human Resilience and practicing kindness and compassion, you can have more meaningful relationships, offer someone words of encouragement, lend them a listening ear, or provide simple strategies.
Emotionally resilient people are often better able to control their emotions, speak clearly, and forge lasting bonds with others. When faced with difficulty, for example, they frequently remain calm, productive, and focused and recover from failures faster than others. People do not naturally possess; instead, it is a talent that can be improved through deliberate practice and constructive coping mechanisms.
What Is Physical Resilience?
This type of Resilience can be described as the body’s capacity to adjust to and tolerate stress, challenges, and changes without suffering harm or harm to itself. It includes preserving or fast regaining bodily health and functionality in the face of hardship, such as injury, disease, or other physical pressures.
Genetics, lifestyle choices, nutrition, exercise, and mental health can influence Physical Resilience. A person’s general health and welfare can be enhanced by developing physical and psychological Resilience, which can aid in injury prevention, sickness recovery, and chronic disease management.
What Is Community Resilience?
Community resilience is the ability of a community to survive and recover from disruptive events such as natural disasters, catastrophes, economic downturns, and social upheaval. It concerns how well a community can react, change, and recover from adversity to emerge more robust and cohesive than before. Building Community Resilience is based on social cohesion, neighborhood networks, and teamwork.
Access to resources and support services, effective communication, and planning for preparation are all necessary components of readiness planning. By building community resilience, individuals, families, and communities better withstand and get over adversity and create a more sustainable and just future.
The Three P’s Of Resilience
The three primary components that go into a person’s explaining style for life events are Seligman’s (1990) 3Ps. The three Ps are:
Personalization
Whether a person assigns herself or other forces as the cause of an occurrence is referred to as personalization. For instance, if a person fails a test, do they place the blame on themselves (“I’m just not smart enough”) or on outside circumstances (“The test was too difficult”)?
Permanence
Whether someone thinks the reason for an event is transient or permanent is referred to as their perception of its permanence. If someone loses their job, for instance, do they think they would never be able to obtain employment again, or do they view it as a temporary setback?
Pervasiveness
The term “pervasiveness” describes whether a person thinks that an event’s cause is particular to one aspect of their life or whether it pertains to all aspects of their existence. For instance, do people think a disagreement with their partner will merely harm their relationship, or do they believe it will affect their lives?
What are the 7 C’s of resilience explained?
Competence, confidence, connection, character, contribution, coping, and control are the seven C’s of resilience. These elements encourage people to become resilient in the face of difficulty. While character, contribution, coping, and control offer resources for overcoming difficult circumstances, competence, confidence, and connection help lay a solid foundation.
What are the five keys to resilience?
These are the five elements of resilience:
Connection: Establishing and upholding enduring connections with others.
Wellness is the maintenance of one’s physical and mental well-being through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and stress reduction methods.
Finding meaning and purpose in your life—through job, hobbies, or volunteer work—is what purpose is all about.
Adaptability is the capacity to change course when circumstances or situations require it.
Maintaining a positive mindset and emphasizing advantages over disadvantages is what is meant by optimism.